
Each October, we donate to breast cancer awareness organizations, wear pink ribbons or clothing, and are grateful for our family members in remission. It’s easy to go through the motions, but it’s more important that we know the risk factors and common signs of breast cancer. Conducting proactive self-breast exams and attending regular doctor appointments can increase the likelihood of detecting your condition early.
About 1 in 8 U.S. women, roughly 13 percent, will develop invasive breast cancer over the course of her lifetime. Additionally, 1 percent of men will develop breast cancer. Considering its commonality, breast cancer is not a disease you want to take lightly.
New research continues to come out so we can act proactively and get diagnosed before it progresses. A study published the Journal of Gynecological Oncology revealed that women with a history of fibroids had a 35 percent higher risk of developing breast cancer when compared to those without uterine fibroids.
Fibroids as Risk Factors for Breast Cancer
Both uterine fibroids and breast cancer are influenced by the body’s estrogen regulation. While they are distinct diseases, their shared risk factors highlight the importance of hormonal balance.
Risk factors that influence your body’s estrogen levels:
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol consumption can increase the risk of breast cancer and uterine fibroids by decreasing folic acid levels which disrupt hormonal balance.
- Obesity and Lack of Physical Activity: Obesity, particularly post-menopausal, combined with a sedentary lifestyle and hormonal imbalances can increase the risk of both breast cancer and uterine fibroids.
- Estrogen Exposure: Women may have prolonged exposure to estrogen from hormone replacement therapy, late menopause, obesity, certain medications, and potentially environmental factors.
- Age Factor: Over a lifetime, women are exposed to estrogen for a longer period, increasing the risk of developing breast cancer.
- Reproductive History: Early onset of menstruation and late menopause expose women to hormones for a longer duration.
Early Warning Signs
Uterine fibroids and breast cancer are the easiest to treat when the condition is detected in its early stages. This is why it’s important to watch for warning signs and discuss with your healthcare provider as symptoms arise.
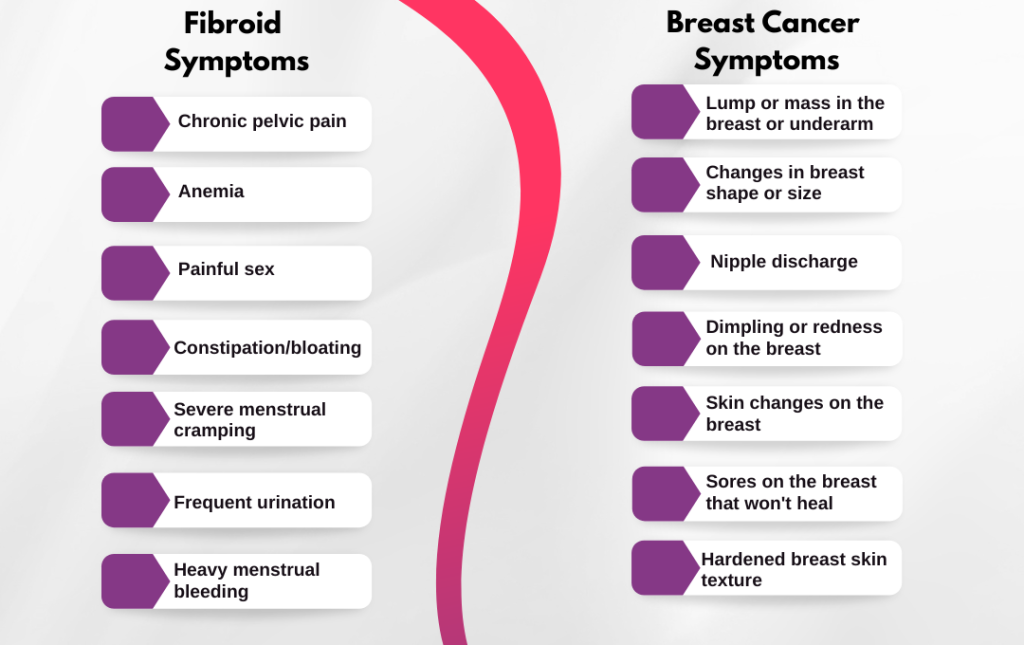
If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen, get ahead of them before they progress.
Proactive Ways to Manage and Treat Fibroids
Fibroid specialists who are interventional radiologists use non-invasive technology like ultrasounds and MRIs to locate fibroid tumors, number and size. Once located, your doctor will work with you to develop a comprehensive fibroid treatment plan that fits your individual needs.
Hysterectomies and invasive surgeries such as myomectomies are not the only options for women with fibroids. There is a non-invasive option called Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) that has a quicker recovery time, preserves fertility and doesn’t require a hospital stay.
At the Fibroid Fighters Foundation, we aim to educate women with fibroids about their options when it comes to finding effective treatment solutions. If you’re experiencing symptoms and want to get checked for fibroids, give us a call at 855-455-5262 or contact us online.
The Fibroid Fighters Foundation is passionate about connecting women with one another to share their unique stories about living with fibroids. If you want to share your fibroid journey and connect with others, check out our testimonial page here where you can talk about your experience via video, audio, or text.
Resources for Breast Cancer Awareness:
https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/types/breast/diagnosis/stages-breast
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2007112-overview
https://www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/diagnosis/hormone_status







