January is Thyroid Awareness Month, and Fibroid Fighters is empowering women to take charge of their health. Discovering the link between thyroid function and fibroid development can lead to a better understanding and management of both conditions, improving women’s well-being.
While the names “fibroids” and “thyroid” sound similar, they are distinct conditions affecting different parts of the body.
- Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop within or on the walls of the uterus.
- Thyroid disease affects the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, just above the collarbone.
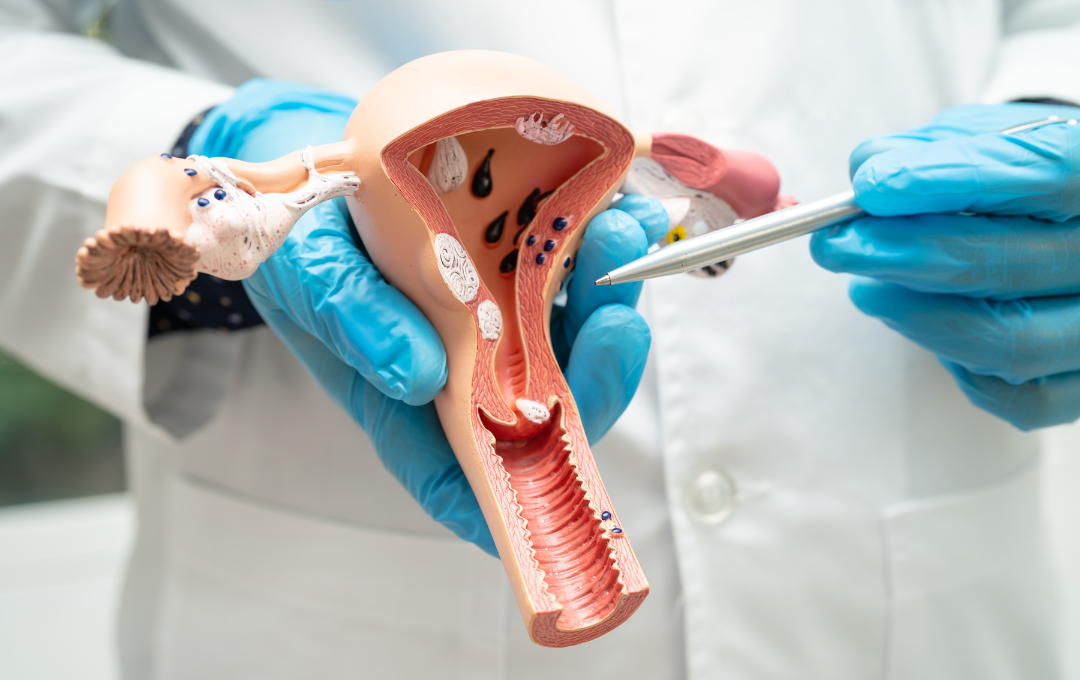
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous tumors in the uterus composed of smooth muscle cells and fibroid connective tissue. Women can have a single fibroid or multiple fibroids that range in size from a seed to a melon.
Fibroid Symptoms
Women diagnosed with fibroids experience a variety of symptoms influenced by their size and location, including:
- Heavy and prolonged periods
- Anemia
- Fatigue
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination
- Constipation and/or bloating
- Pain in your pelvis or lower back
- Increased menstrual cramping
- Stomach swelling
These symptoms can range from mild to severe. If symptoms disrupt your life or cause debilitating pain, it may be time to schedule a fibroid consultation.
Curious? Take Our Symptom Checker
According to studies, uterine fibroids occur in 17.6% of women with thyroid nodules.
National Institute of Health
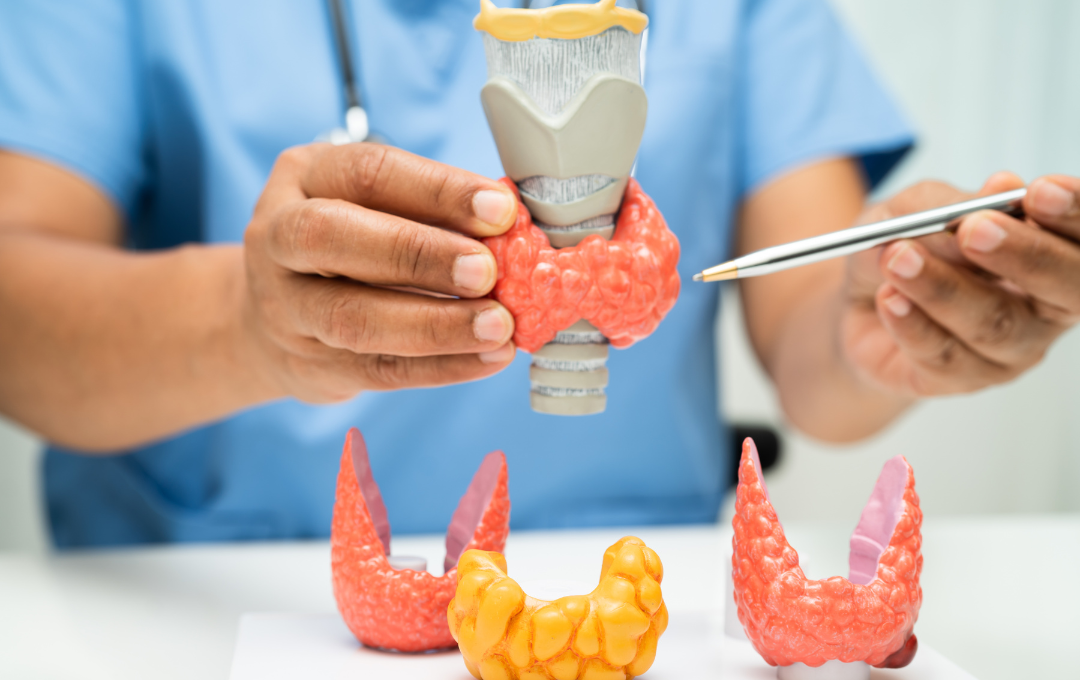
Thyroids
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, and heart rate. Thyroids can even influence factors like breathing, strength, cholesterol levels, and the functioning of both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Thyroid Disease Symptoms
Thyroid disease refers to a number of conditions that affect how the gland functions. The thyroid can be either overactive or underactive and both conditions can lead to health problems. Two of the most common thyroid diseases are hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
HYPERTHYROIDISM
Also known as overactive thyroid disease, this condition occurs when your thyroid gland produces excess levels of the thyroid hormone thyroxine. This thyroid disease can increase your body’s metabolism, causing weight loss and an irregular heartbeat.
HYPOTHYROIDISM
Having an underactive thyroid is known as hypothyroidism. Essentially, this condition occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Women are more likely to be affected than men by hypothyroidism, this increased risk is largely attributed to the impact of female sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone on thyroid function. According to the Office on Women’s Health, for every eight women, at least one will likely have some form of thyroid disease.
Hypothyroidism’s deficiency of thyroid hormones can disrupt things such as heart rate, body temperature, and all aspects of metabolism. Major symptoms include fatigue, cold sensitivity, constipation, dry skin, and unexplained weight gain.
Symptoms of thyroid disease can include:
- Weight Fluctuation: Unexplained weight gain or loss despite a normal diet or increased appetite.
- Energy Levels: Fatigue, constant tiredness, and lack of energy or increased energy, restlessness, and difficulty sleeping (insomnia).
- Temperature Sensitivity: Intolerance to cold, feeling unusually sensitive to cold temperatures or heat intolerance, feeling overly sensitive to heat and sweating excessively.
- Bowel Habits: Constipation, difficulty in passing stool or diarrhea, frequent loose or watery stools.
- Heart Rate: Slow heart rate or rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) and palpitations.
- Mood Changes: Depression, feeling persistently sad, hopeless, and disinterested or anxiety, irritability, feeling restless, nervous, and easily agitated.
- Hair and Skin: Dry skin, hair loss, thinning hair, especially on the scalp.
- Voice Changes: Hoarse voice, a deeper or rougher voice than usual.
- Muscle Strength: Muscle weakness, difficulty with everyday activities that require muscle strength.
- Goiter: Noticeably enlarged or swollen thyroid gland.
Overlapping Symptoms Between Fibroid and Thyroid Disease

One overlapping symptom of both thyroid disease and uterine fibroids is abnormal, heavy menstrual bleeding. This can also lead to fatigue and anemia in both conditions.
Regardless of the underlying cause, experiencing any of these symptoms warrants a medical evaluation. While over-the-counter remedies like ibuprofen and heating pads may temporarily alleviate discomfort associated with heavy bleeding, it’s crucial to address the root cause of the issue.
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to determine the underlying condition and receive appropriate treatment.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase a woman’s risk of developing uterine fibroids. These include biological factors such as a family history of fibroids and a high body mass index (BMI). Lifestyle factors, such as alcohol consumption and the use of oral contraceptives (birth control pills), may also play a role in fibroid development.
While not a direct risk factor for fibroids, anemia is a common symptom of both fibroid-related heavy bleeding and certain thyroid conditions. Therefore, women with a history of fibroids may have an increased risk of developing thyroid issues.
Both uterine fibroids and thyroid nodules are influenced by estrogen and prevalent among women of reproductive age.
Pregnancy Problems
Both thyroid disease and uterine fibroids can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage, preterm birth and placental problems. Untreated thyroid conditions can also affect the baby’s development. If you have either condition, close monitoring or management during pregnancy are crucial for optimal outcomes.
Treatments
Uterine fibroids can be treated with various methods, including minimally invasive procedures like uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), which blocks blood flow to the fibroids causing them to shrink. Surgical options range from myomectomy to hysterectomy. Hormonal therapies and endometrial ablation are also available to manage symptoms like heavy bleeding.
Thyroid disease treatments truly depend on the sort of problem a person may have. Hypothyroidism is normally treated with hormone medications, whereas hyperthyroidism may need more action, such as radioiodine, surgery, and medicine.
The best treatment choice depends on individual factors and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Awareness
At the Fibroid Fighters Foundation, we aim to educate women with fibroids about their options when it comes to finding effective treatment solutions. If you’re experiencing symptoms and want to get checked for fibroids, give us a call at 855-455-5262 or contact us online.
The Fibroid Fighters Foundation is passionate about connecting women with one another to share their unique stories about living with fibroids. If you want to share your fibroid journey and connect with others, check out our fibroid testimonial page here where you can talk about your experience via video, audio, or text.







